Chelsea PTO Troubleshooting
The Chelsea P.T.O. is designed and built to meet the rugged demands of the Mobile Equipment Industry. Continue reading for information on diagnostics for your PTO troubleshooting needs. If you need additional assistance give us a call at 877-776-4600 or 407-872-1901, to speak with a Chelsea PTO expert.
You can view this PTO troubleshooting information in PDF format by clicking here.
You can also view our selection of Chelsea PTO parts manuals by visiting our manuals page.

Chelsea P.T.O.s are designed and built to match a vehicle’s transmission. The gears of a P.T.O. are of the same quality as the transmission’s gears. Successful operation depends on proper specification and installation. Always consult your Chelsea Applications Guide and Installation Manual when working with Chelsea P.T.O.s. Doing this will prevent serious P.T.O. problems.
 WARNING!
WARNING!

PTO Troubleshooting On The Vehicle:
Performance
The first place to look when troubleshooting a P.T.O. failure is in the application itself.
Repeated or premature failure may be a sign of an incorrect application.
This can be discovered by using
HY25-3000/US Applications Catalog.
If the P.T.O. was correctly specified and then failed prematurely, there are two likely causes:
- Improper installation and/or operator misuse.
- An improperly installed P.T.O. can normally be identified immediately by the sound (Noise) it makes.
• It will “Whine” ,“Clatter”, “Click” or “Grind”
• Sometimes, the vehicle itself may contribute enough noise to mask the sound of the P.T.O. and one may not notice the problem
If a problem is allowed to continue, damage to the P.T.O. will result.
Noise Types:
Set gear backlash min. to .006 – .012.
- Whine – Too tight
- Clatter – Too loose

- Clicking or Grinding
Leaks – Root Cause of the Leakage
Stud Threads
- Improper Torque of Fasteners
- Improper Stud Installation
- Gasket Installation
Seals
- Transmission Preparation
- Worn Seals
PTO Troubleshooting On The Workbench:
Performance – Symptoms & Causes
P.T.O. Operation – Hydraulic System

- Erratic Operation
- Hard Shifting
- Jumping out of Gear
Items to be Examined on the Work Bench
- Housing
- Gears
- Shafts
- Bearings
- Shifters
- Clutches
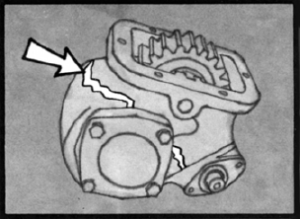
Housing Damage
One of the most serious problems a P.T.O. can suffer is a cracked case. This condition can lead to oil loss and eventual transmission failure.
Some causes are:
- Improper Installation
- Poorly Torqued Bolts
- Unsupported Direct Mount Pump
- Foreign Objects Meshing Between the Gear Teeth
- Severe Shock Load
- Hitting Obstacles in the Road
- Damaged Threads

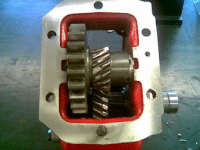
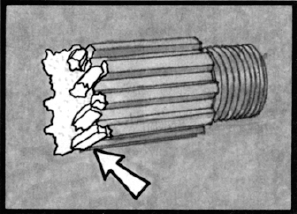
Gear Damage
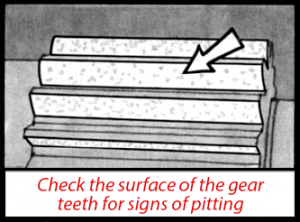
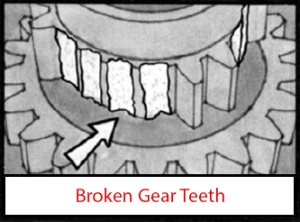
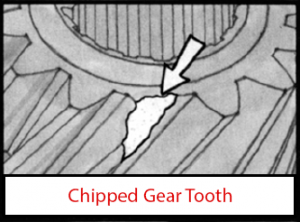
PTO gear damage generally takes place in the tooth or spline. The first parts to inspect should be the gears. Check the surface of the gear teeth for signs of pitting. Once pitting of the gear surfaces has begun, there is nothing that can stop it. Another possible problem during vehicle operation is “shock load”. Deep Mesh Pattern Caused by Improper Backlash Adjustment. Worn PTO gears can easily be affected by “shock load”. If you neglect to replace gears that are worn, they can eventually lead to broken gear teeth. Sometimes a gear will chip a tooth because of mishandling or improper shifting. Undershifting allows incomplete gear tooth contact with the driver gear. This means only part of the tooth width is transmitting the torque and R.P.M. during P.T.O. operation.
Shaft Damage
P.T.O. shafts are also vulnerable to operating abuse, torsional overload, bending fatigue failure.
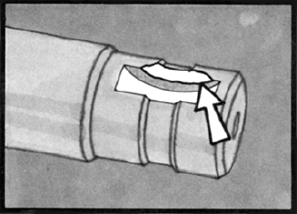
When inspecting a P.T.O. output shaft, always inspect the keyway.
PTO shaft damage can occur misapplication overloads and shock loads.
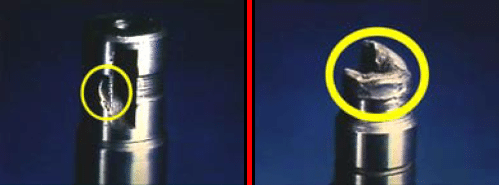
Fretting corrosion is another type of damage your PTO shafts can experience. It appears as a rusting and wearing of the pump shaft splines. Fretting corrosion is caused by many factors and without proper maintenance, the anti-fretting grease can only reduce, but not eliminate, its effect on components.


Shifting Problems

If you experience that your P.T.O. is hard to shift, remember, a lever-operated shift linkage should not be connected to a wire shift cover. The mechanical advantage of the lever is often too great for the wire shift cover and could severely damage it. Also inversely, don’t use a cable with a lever shift cover. The cable isn’t capable of transmitting the force necessary to shift a lever mechanism.

Most shifting complaints are caused by improper shifting procedure or incorrect linkage installation.
Shifting problems can also be caused by a worn or elongated shifter poppet hole.

Seals and O-Rings may cause special problems in P.T.O. operations.

Remember, when troubleshooting any clutch-operated P.T.O., carefully inspect all components for wear or damage. Burnt clutch plates, welded clutch pack, or a burnt driving hub are three easily identifiable conditions that lend themselves to failure analysis.
A sure sign of potential trouble with a clutch operated P.T.O. is erratic operation.
The 3 most common complaints:
Noise
Listen carefully for a whine or high pitched sound. This could indicate issues with the gears being too tight, bearings or hydraulics. A rattle could indicate issues with the gears too loose or torsional vibrations.
Engagement Problems
Powershift PTO engagement problems could be from blocked hoses or fittings, bad connections or ground or the solenoid. Mechanical PTO engagement problems could originate from low air pressure, improper cable installation or back lash too tight.
Disengagement Problems
Experiencing disengagement problems with powershift PTOs could indicate issues with blocked hoses or fittings, frozen clutch pack or the solenoid.
Prevention
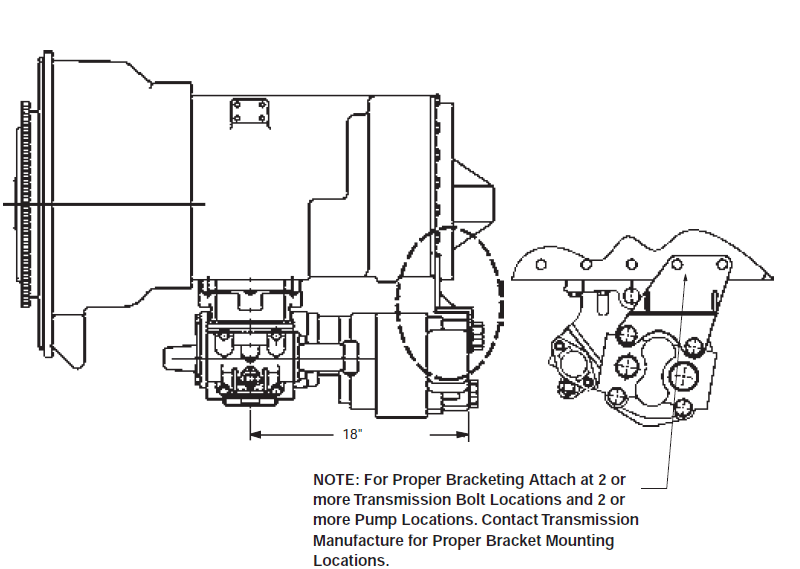
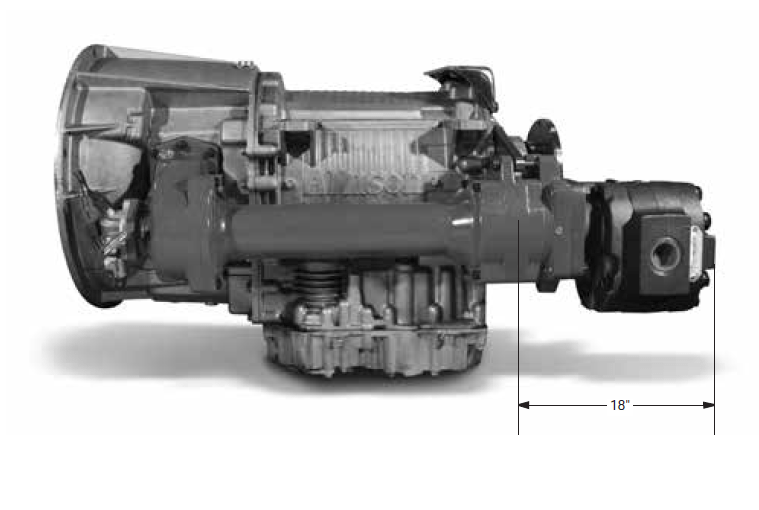
Chelsea strongly recommends the use of pump supports (Support Brackets) in all applications. Also remember to pack the female pilot of the PTO pump shaft with grease before installing the pump on the PTO.
Chelsea PTOs are designed and built to match a vehicle’s transmission, the gears of a PTO are of the same quality as the transmission’s gears. Successful operation depends on proper specification and installation.